ASH FUSION TEMERATURE
What Is ASH FUSION TEMPERATURE ?
Ash Fusion Temperature (AFT) is an important property of coal, which is the temperature at which the ash residue from burning coal starts to soften and fuse together. The AFT is typically determined by heating a sample of coal in a high-temperature furnace, and observing the behavior of the ash residue.
The AFT is an important parameter in the design and operation of coal-fired power plants, as it can affect the performance of the combustion process and the efficiency of the boiler. If the AFT is too low, the ash residue can become sticky and cause problems such as slagging and fouling in the boiler. On the other hand, if the AFT is too high, the ash may not fuse together sufficiently and can be carried away by the flue gas, resulting in increased emissions.
The AFT can vary widely depending on the composition and properties of the coal. Generally, higher ash content coals tend to have higher AFT values. The AFT of coal can be classified into several temperature ranges, including
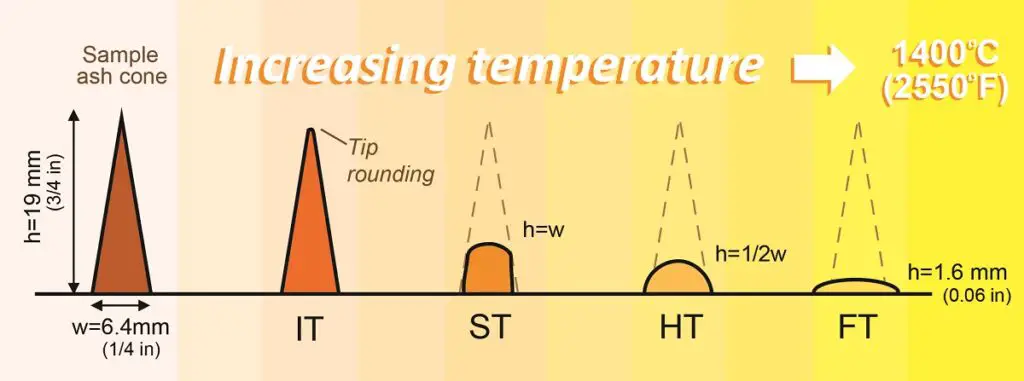
Initial Deformation Temperature (IDT)
The temperature at which the ash starts to soften and deform the cone.
Softening Temperature
The temperature at which cone forms more deform and soften than the IDT.
Hemispherical Temperature (HT)
the temperature at which the ash forms a hemispherical shape.
Fluid Temperature (FT)
The temperature at which the ash becomes fully fluid and can flow like a liquid.
Ash Fusion Temperature (AFT)
The temperature at which the ash forms a solid mass.
AFT testing is typically performed on coal samples using specialized laboratory equipment, such as the Ash Fusion Tester. The results of AFT testing can be used to select coals with appropriate properties for specific applications and to optimize the performance of coal-fired power plants.
Types of AFT Instruments
Ash Fusion Temperature (AFT) instruments are specialized laboratory equipment used to determine the ash fusion temperature of coal and other solid fuels. AFT instruments are important in the evaluation of coal and other fuels for use in industrial processes, particularly in coal-fired power plants.
There are several types of AFT instruments available, each with its own specific method of operation and features. Some of the most common types of AFT instruments are:
- Ash Fusion Tester: The Ash Fusion Tester is a widely used instrument that uses a high-temperature furnace to heat a sample of coal or other fuel to the point of ashing. The instrument then measures the temperature at which the ash residue begins to soften and fuse together, providing a range of AFT temperatures.
- Dilatometer: The Dilatometer is another type of AFT instrument that measures the deformation of a sample of coal or other fuel as it is heated in a furnace. The instrument measures the sample’s contraction or expansion as it is heated, allowing for the determination of the AFT.
- Furnace Camera: Some AFT instruments utilize a camera to record the behavior of the sample as it is heated, allowing for real-time observation of the ash fusion process.
- Laser AFT: Laser AFT is a newer type of AFT instrument that uses a laser to measure the deflection of a sample as it is heated. This allows for a more precise determination of the AFT and can provide detailed information on the properties of the ash residue.
AFT instruments are essential in evaluating the suitability of coal and other solid fuels for use in industrial processes. By providing accurate measurements of the AFT, these instruments can help to optimize the performance and efficiency of coal-fired power plants and other industrial processes that rely on solid fuels.
Price ranges of AFT Instruments are 20 L to 45 L depends of the dealing of instruments with supplier. but good range instrument you will get up to 30-35 L.
